- Diamond under the microscope -
The famous 4cs
Discover all about the properties of diamonds and learn more about Cut, Colour, Carat and Clarity .
1.Cut
Cut is perhaps the most important property of a diamond. A well-cut stone looks bigger, brighter and more radiant. Moreover, this is the only quality that can be influenced by man.
The cut does not say anything about the shape of the diamond (round, princess, emerald, pear), but only about the balance between proportion, symmetry and shine achieved by the diamond cutter. The closer to perfection this is, the more a diamond will shine. Essentially, the cut quality determines how effectively light entering the diamond is refracted into the stone and reflected back off the top of the diamond. A poorly cut stone is often too deep or too superficial, so that most of the light escapes and the diamond looks dark and barely sparkles. That is why we only use diamonds with a 'very good' cut or higher for the Aurore jewellery.
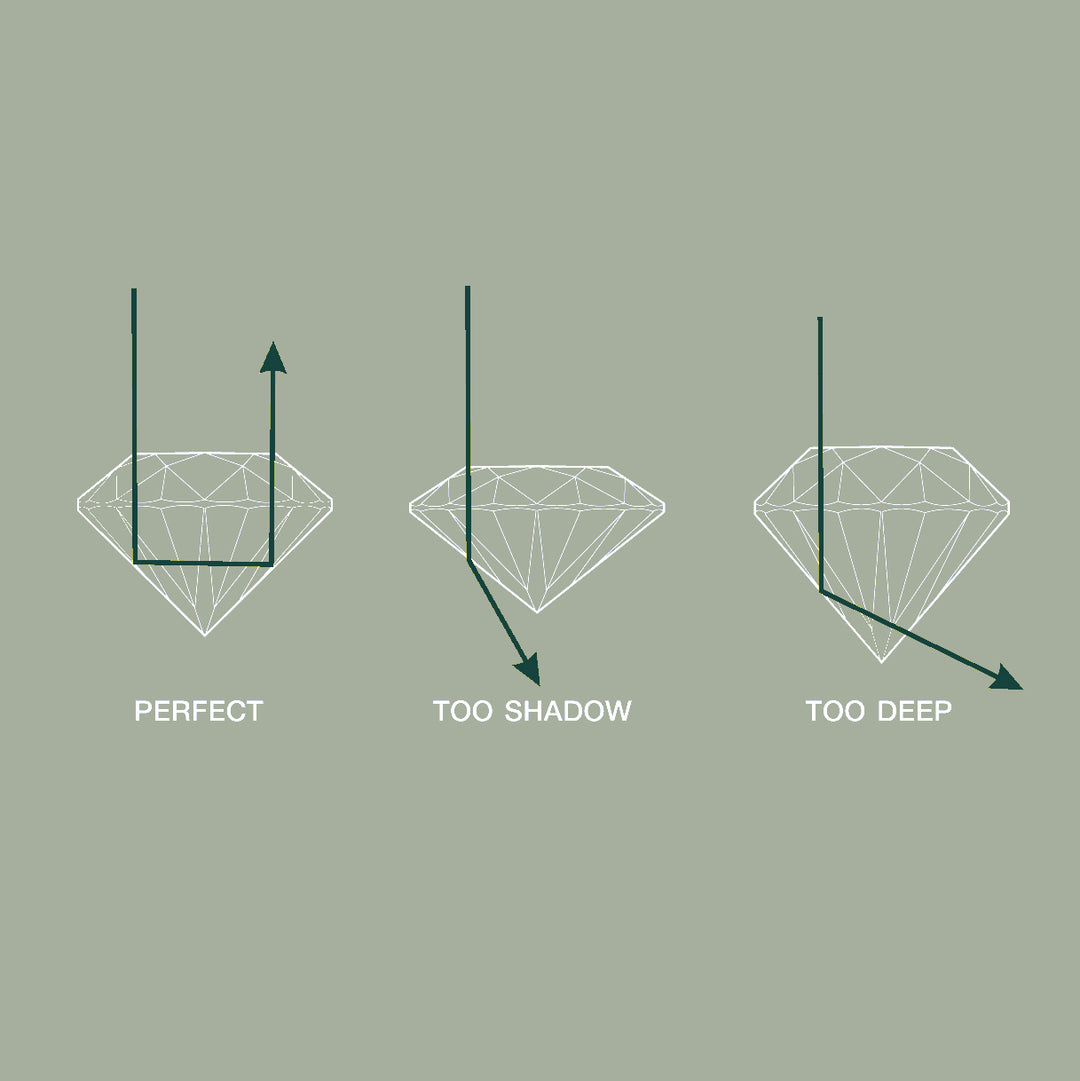
Diamond & light
The way light affects the diamond is often divided into the following three categories:
Reflection Part of the light is reflected directly from the top (table) of a diamond.
Diffusion Shows how light travels inside the diamond and is reflected off the cut facets. The better the distribution of the facets, the better the light is reflected by the diamond.
Refraction Light enters through the top of the diamond, is refracted into a rainbow of colors and then reflected back and forth by mirroring against the facets. When it leaves the diamond's crown again, the colors remain separate, so your eye perceives a rainbow of colors. This is also called fire.
2. Colour
When you talk about diamond color, this has a different meaning with fancy colored diamonds than with white diamonds. In the latter case, it is actually about the absence of color.
The color is graded internationally from D (completely colorless) to Z (yellow). In this case, the colorless diamonds are the rarest and therefore the most expensive.
Brilliant colours
Diamonds with less color let more light through, releasing more sparkle and fire. As can be read above, a diamond works like a prism and reflects the light as colorful flashes called fire. Just like when you look through a colored glass, a diamond with more color will act as a filter and therefore reduce the reflected color spectacle or fire. A diamond with a higher color quality, i.e. a whiter stone, shows more colorful fire. We only work with diamonds with a G color or higher.

3.Clarity
Clarity says something about the clarity of a diamond and the possible presence of inclusions. Almost all diamonds have some form of inclusions. These features on the surface and inside the stone are inspected by gemmologists who use a 10x magnification to assign a clarity grade to the diamond. The number of imperfections, their position and size ultimately determine the degree. Diamonds with no or very few inclusions are considered extremely rare and are therefore very expensive.
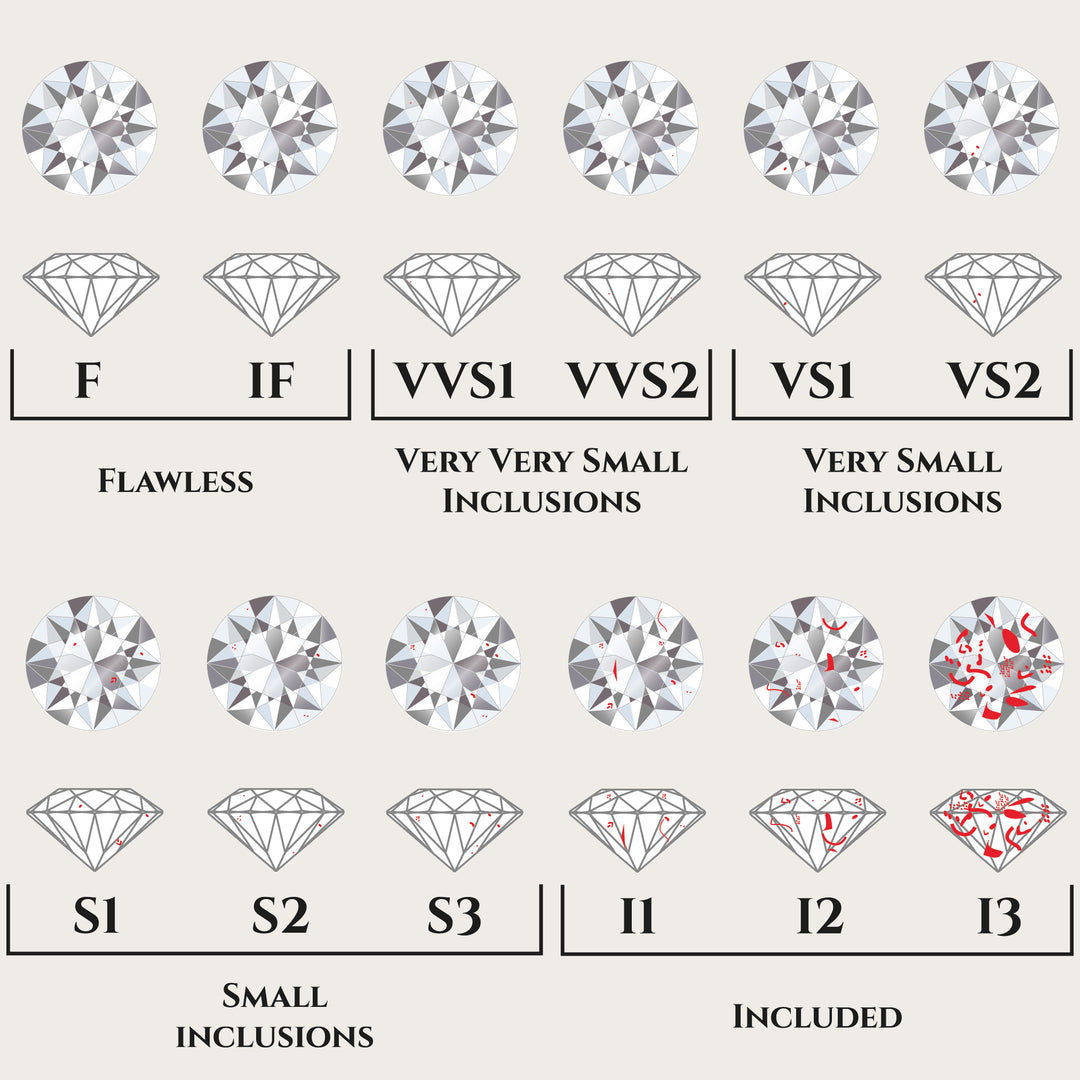
What clarity do you want?
Most experts agree that clarity has the least impact on a diamond's appearance, as long as it is visually clean. This actually applies to all diamonds with an SI2 classification or higher. Diamonds that are graded lower usually have imperfections that are easily visible to the naked eye. We therefore only use diamonds with a clarity of SI2 or higher for our jewelry.
4. Carat
Carat indicates the weight unit of diamonds. Here, 1 carat equals 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams. When people talk about the diamond weight, they often talk about 'points'. 1 point is equal to 0.01 carat and 100 points is therefore 1 carat.
Carat comes from the word carob, or carob trees. Long ago, the seeds of these trees were used as a counterweight for weighing diamonds, gems and precious metals, as they were thought to have the same mass.

Bigger is better?
When selecting a diamond, the number of carats is often the only consideration. It is important to know that the carat weight is not equal to the size of a diamond. Depending on, among other things, the cut, a stone of 0.90 carat can look larger than one of 1 carat.
If the other properties of the diamond are equal, a larger diamond is always more valuable than a smaller variant. Larger diamonds are much rarer than smaller ones and the price increases exponentially. This means that a 1 ct diamond is more than twice as valuable as a 0.5 ct stone.








